Opponents
of empiricism and science have long asked, “When a human sees things in the
real world and spots patterns in the events going on there, then makes
statements about what she is spotting, what
is doing the spotting? The human mind, and the sense data–processing
programs it must already contain to be able to do the tricks empiricists
describe, obviously came before any data processing could be done. What is this
equipment, and how does it work?” Philosophers of science have had trouble
explaining what this mind that does the knowing is, and thus what science,
the most rigorous form of knowing, is and is trying to do.
Consider
what science is aiming to achieve. What scientists want to discover, come to
understand, and then use in creative ways in the real world are what are
usually called the “laws of nature”. Scientists do more than simply observe the
events in physical reality. They also strive to understand how these events
come about and then to express what they understand in general statements about
these events, in mathematical formulas, in chemical formulas, in rigorously
logical sentences in one of the world’s many languages, or in some other symbol
system used by people for conveying their thoughts to other humans. A “natural
law” statement must describe one of the ways in which reality works, and, to be
considered scientific, the statement must be set down in such a way that it can
be tested in the real world.
If claims
about this newly discovered real-world truth are going to be worth considering,
scientists must be able to test those claims in some real, material way. Thus,
any natural law statement that is made, to be of any practical use whatever and
to stand any chance of enduring, must first be expressed in some language or
symbol system that humans use to communicate ideas with other humans. A theory
or model that can be expressed only inside the head of its inventor will die
with her or him.
The following is a verbal statement of Newton’s
law of universal gravitation: “Any two bodies in the universe attract each
other with a force that is directly proportional to the product of their masses
and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them.”
In contrast, the
mathematical formula expressing Newton’s law of universal gravitation looks
like this:
And
consider another example:
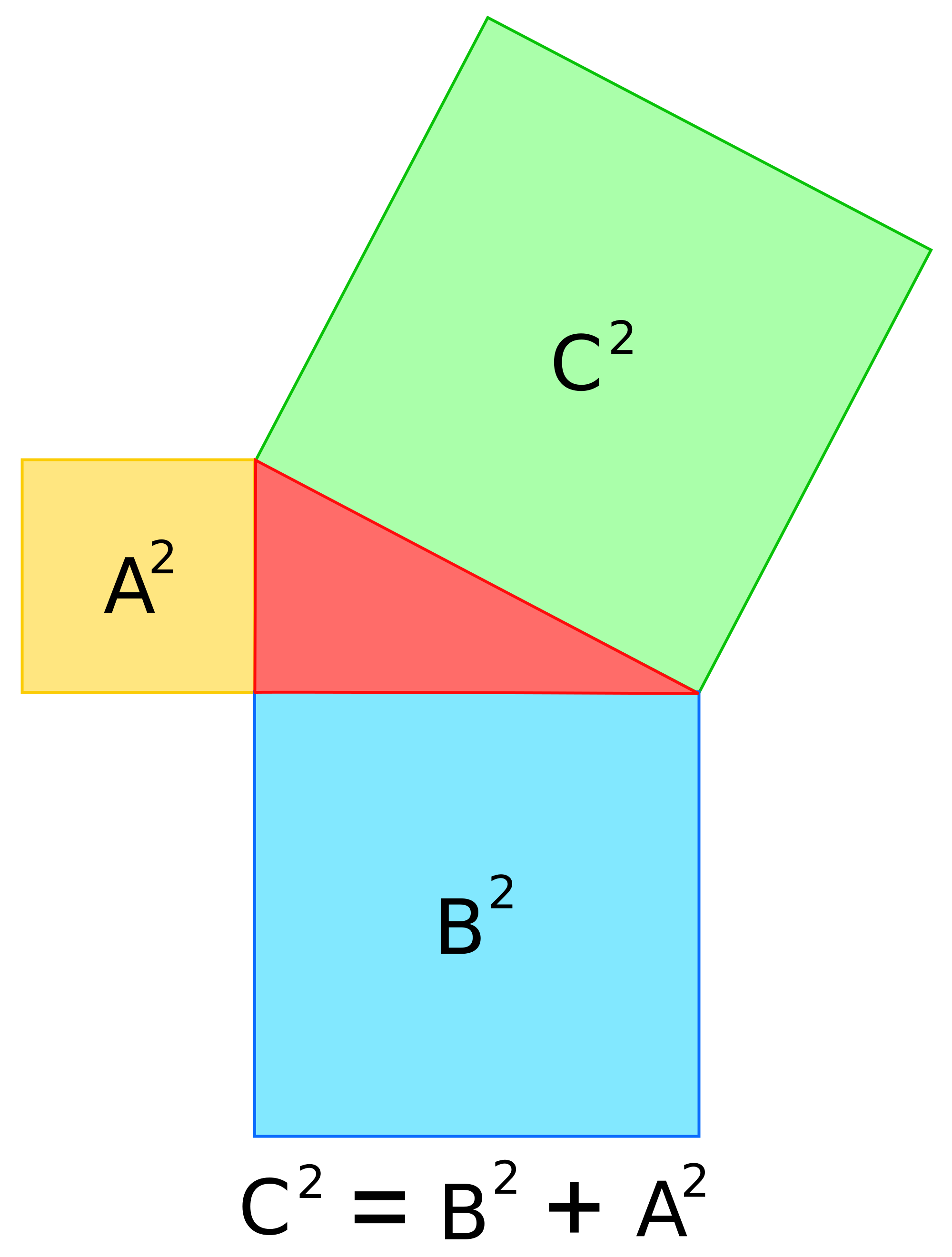
The
Pythagorean theorem is a mathematical law, but is it a scientific one? Can it
be tested in some absolutely unshakable way in the real world? (Hint: How can
you measure the sides and know you’re exactly accurate?)
The
big problem occurs when we try to analyze logically just how true statements
like Newton’s laws of motion or Darwin’s theory of evolution are. Do statements
of these laws express unshakable truths about the real world or are they just temporarily
useful ways of roughly describing what appears to be going on in
reality – ways that are followed for a few decades while the laws appear to work for scientists, but that then are revised or
dropped when new problems they can’t explain are encountered?
Many
scientific theories in the last four hundred years have been revised or dropped
altogether. Do we dare to say about any scientific law statement that it is true
in the unassailable way in which 5 + 7 = 12 is true or the Pythagorean theorem
is true?
This
debate is a hot one in Philosophy right up to the present time. Many
philosophers of Science claim that scientific laws, once supported by enough experimental evidence, can be considered to be true in the
same way as valid math theorems are. But there are also many who say the
opposite —all scientific law statements are tentative. These people believe
that, given time, all such statements get replaced by new statements based on
new models or theories.
No comments:
Post a Comment
What are your thoughts now? Comment and I will reply. I promise.